OOM问题分析
简介
OOM(OutOfMemoryError),最近线上版本出现了大量线程OOM的crash,尤其是华为Android 9.0系统的手机,占总OOM量的85%左右。
内存指标概念
- USS(Unique Set Size): 物理内存,进程独占的内存
- PSS(Proportional Set Size): 物理内存,PSS = USS + 按比例包含共享库
- RSS(Resident Set Size): 物理内存,RSS = USS + 包含共享库
- VSS(Virtual Set Size): 虚拟内存,VSS = RSS + 未分配实际物理内存
OOM分类
[XXXClassName] of length XXX would overflow“是系统限制String/Array的长度所致,这种情况比较少。
java.lang.OutOfMemoryError: "Failed to allocate a " << byte_count << " byte allocation with " << total_bytes_free << " free bytes and " << PrettySize(GetFreeMemoryUntilOOME()) << " until OOM";
通常情况下是因为java堆内存不足导致的,即Runtime.getRuntime().maxMemory()获取到的最大内存无法满足要申请的内存大小时,这种情况比较好模拟,例如我们可以通过new byte[]的方式来申请超过maxMemory()的内存,但是也有一些情况是堆内存充裕,而且设备内存也充裕的情况下发生的。
java.lang.OutOfMemoryError: Could not allocate JNI Env(代号JNIEnv)
- cat /proc/pid/limits 描述linux系统对对应进程的限制:
里面Limit Soft Limit Hard Limit Units Max cpu time unlimited unlimited seconds Max file size unlimited unlimited bytes Max data size unlimited unlimited bytes Max stack size 8388608 unlimited bytes // 整个系统的 Max core file size 0 unlimited bytes Max resident set unlimited unlimited bytes Max processes 17235 17235 processes // 整个系统的最大进程数,底层只有进程,线程也是通过进程实现的 Max open files 32768 32768 files // 每个进程最大打开文件的数量 Max locked memory 67108864 67108864 bytes // 线程创建过程中分配线程私有stack使用的mmap调用没有设置MAP_LOCKED,所以这个限制与线程创建过程无关 Max address space unlimited unlimited bytes Max file locks unlimited unlimited locks Max pending signals 17235 17235 signals // c层信号个数阈值,与线程创建过程无关 Max msgqueue size 819200 819200 bytes Max nice priority 40 40 Max realtime priority 0 0 Max realtime timeout unlimited unlimited usMax open files表示每个进程最大打开文件的数目,进程每打开一个文件就会产生一个文件描述符fd(记录在/proc/pid/fd中)
验证: 触发大量的网络连接或者打开文件,每个连接处于独立的线程中并报出,每打开一个socket都会增加一个fd
private Runnable increaseFDRunnable = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
new BufferedReader(new FileReader("/proc/" + Process.myPid() + "/status"));
}
Thread.sleep(Long.MAX_VALUE);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
};
java.lang.OutOfMemoryError: pthread_create(1040KB statck) failed: Out of memory(代号1040)
根据OOM的crash日志,我们发现都是从Thread.start()方法开始的,
public synchronized void start() {
/**
* This method is not invoked for the main method thread or "system"
* group threads created/set up by the VM. Any new functionality added
* to this method in the future may have to also be added to the VM.
*
* A zero status value corresponds to state "NEW".
*/
// Android-changed: throw if 'started' is true
if (threadStatus != 0 || started)
throw new IllegalThreadStateException();
/* Notify the group that this thread is about to be started
* so that it can be added to the group's list of threads
* and the group's unstarted count can be decremented. */
group.add(this);
started = false;
try {
nativeCreate(this, stackSize, daemon);
started = true;
} finally {
try {
if (!started) {
group.threadStartFailed(this);
}
} catch (Throwable ignore) {
/* do nothing. If start0 threw a Throwable then
it will be passed up the call stack */
}
}
}
上面的核心方法是nativeCreate(this, stackSize, daemon);
这个方法有三个参数:
- this : Thread对象自身
- stackSize : the desired stack size for the new thread, or zero to indicate that this parameter is to be ignored.该新创建的线程的栈的大小,单位是byte,一般默认情况下都是0,我们全局搜这个变量复制的地方,可以看到Thread有一个构造函数可以设置这个值
public Thread(ThreadGroup group, Runnable target, String name, long stackSize) { init(group, target, name, stackSize); } - daemon : Whether or not the thread is a daemon thread.
而nativeCreate方法的native实现,是在art/runtime/native/java_lang_thread.cc中,因为OOM主要是在Android 9.0系统发生,所以这里基于9.0系统的源码分析:https://android.googlesource.com/platform/art/+/refs/tags/android-9.0.0_r41/runtime/native/java_lang_Thread.cc。
static void Thread_nativeCreate(JNIEnv* env, jclass, jobject java_thread, jlong stack_size,
jboolean daemon) {
// There are sections in the zygote that forbid thread creation.
Runtime* runtime = Runtime::Current();
if (runtime->IsZygote() && runtime->IsZygoteNoThreadSection()) {
jclass internal_error = env->FindClass("java/lang/InternalError");
CHECK(internal_error != nullptr);
env->ThrowNew(internal_error, "Cannot create threads in zygote");
return;
}
Thread::CreateNativeThread(env, java_thread, stack_size, daemon == JNI_TRUE);
}
里面又会调用到art/runtime/thread.cc中的Thread::CreateNativeThread方法:
void Thread::CreateNativeThread(JNIEnv* env, jobject java_peer, size_t stack_size, bool is_daemon) {
CHECK(java_peer != nullptr);
Thread* self = static_cast<JNIEnvExt*>(env)->GetSelf();
if (VLOG_IS_ON(threads)) {
ScopedObjectAccess soa(env);
ArtField* f = jni::DecodeArtField(WellKnownClasses::java_lang_Thread_name);
ObjPtr<mirror::String> java_name =
f->GetObject(soa.Decode<mirror::Object>(java_peer))->AsString();
std::string thread_name;
if (java_name != nullptr) {
thread_name = java_name->ToModifiedUtf8();
} else {
thread_name = "(Unnamed)";
}
VLOG(threads) << "Creating native thread for " << thread_name;
self->Dump(LOG_STREAM(INFO));
}
Runtime* runtime = Runtime::Current();
// Atomically start the birth of the thread ensuring the runtime isn't shutting down.
bool thread_start_during_shutdown = false;
{
MutexLock mu(self, *Locks::runtime_shutdown_lock_);
if (runtime->IsShuttingDownLocked()) {
thread_start_during_shutdown = true;
} else {
runtime->StartThreadBirth();
}
}
if (thread_start_during_shutdown) {
ScopedLocalRef<jclass> error_class(env, env->FindClass("java/lang/InternalError"));
env->ThrowNew(error_class.get(), "Thread starting during runtime shutdown");
return;
}
// 1. native层创建thread
Thread* child_thread = new Thread(is_daemon);
// Use global JNI ref to hold peer live while child thread starts.
child_thread->tlsPtr_.jpeer = env->NewGlobalRef(java_peer);
// 2. FixStackSize方法里面会返回具体的Stack内存的大小
stack_size = FixStackSize(stack_size);
// Thread.start is synchronized, so we know that nativePeer is 0, and know that we're not racing
// to assign it.
env->SetLongField(java_peer, WellKnownClasses::java_lang_Thread_nativePeer,
reinterpret_cast<jlong>(child_thread));
// 3. java中的每一个线程都都应一个JNIEnv结构,这里的JNIEnvExt就是ART中的JNIEnv。下面的注释说明的很明白,这里可能会有oom
// Try to allocate a JNIEnvExt for the thread. We do this here as we might be out of memory and
// do not have a good way to report this on the child's side.
std::string error_msg;
std::unique_ptr<JNIEnvExt> child_jni_env_ext(
JNIEnvExt::Create(child_thread, Runtime::Current()->GetJavaVM(), &error_msg));
int pthread_create_result = 0;
if (child_jni_env_ext.get() != nullptr) {
// 4. child_jni_env_ext.get() != nullptr 才会继续
pthread_t new_pthread;
pthread_attr_t attr;
child_thread->tlsPtr_.tmp_jni_env = child_jni_env_ext.get();
CHECK_PTHREAD_CALL(pthread_attr_init, (&attr), "new thread");
CHECK_PTHREAD_CALL(pthread_attr_setdetachstate, (&attr, PTHREAD_CREATE_DETACHED),
"PTHREAD_CREATE_DETACHED");
CHECK_PTHREAD_CALL(pthread_attr_setstacksize, (&attr, stack_size), stack_size);
// 5. 调用pthread_create创建线程,并返回结果
pthread_create_result = pthread_create(&new_pthread,
&attr,
Thread::CreateCallback,
child_thread);
CHECK_PTHREAD_CALL(pthread_attr_destroy, (&attr), "new thread");
if (pthread_create_result == 0) {
// 6. 结果为0才是创建成功
// pthread_create started the new thread. The child is now responsible for managing the
// JNIEnvExt we created.
// Note: we can't check for tmp_jni_env == nullptr, as that would require synchronization
// between the threads.
child_jni_env_ext.release();
return;
}
}
// Either JNIEnvExt::Create or pthread_create(3) failed, so clean up.
{
MutexLock mu(self, *Locks::runtime_shutdown_lock_);
runtime->EndThreadBirth();
}
// Manually delete the global reference since Thread::Init will not have been run.
env->DeleteGlobalRef(child_thread->tlsPtr_.jpeer);
child_thread->tlsPtr_.jpeer = nullptr;
delete child_thread;
child_thread = nullptr;
// TODO: remove from thread group?
env->SetLongField(java_peer, WellKnownClasses::java_lang_Thread_nativePeer, 0);
{
std::string msg(child_jni_env_ext.get() == nullptr ?
StringPrintf("Could not allocate JNI Env: %s", error_msg.c_str()) :
// 具体的错误信息由pthread_create_result的返回的错误码给出。
StringPrintf("pthread_create (%s stack) failed: %s",
PrettySize(stack_size).c_str(), strerror(pthread_create_result)));
ScopedObjectAccess soa(env);
soa.Self()->ThrowOutOfMemoryError(msg.c_str());
}
}
上面代码太多,分了四个部分:
- native层创建thread
- FixStackSize方法里面会返回具体的Stack内存的大小
static size_t FixStackSize(size_t stack_size) { // A stack size of zero means "use the default". if (stack_size == 0) { stack_size = Runtime::Current()->GetDefaultStackSize(); } // Dalvik used the bionic pthread default stack size for native threads, // so include that here to support apps that expect large native stacks. stack_size += 1 * MB; // It's not possible to request a stack smaller than the system-defined PTHREAD_STACK_MIN. if (stack_size < PTHREAD_STACK_MIN) { stack_size = PTHREAD_STACK_MIN; } if (Runtime::Current()->ExplicitStackOverflowChecks()) { // It's likely that callers are trying to ensure they have at least a certain amount of // stack space, so we should add our reserved space on top of what they requested, rather // than implicitly take it away from them. // 8k stack_size += GetStackOverflowReservedBytes(kRuntimeISA); } else { // If we are going to use implicit stack checks, allocate space for the protected // region at the bottom of the stack. // 8k 8k stack_size += Thread::kStackOverflowImplicitCheckSize + GetStackOverflowReservedBytes(kRuntimeISA); } // Some systems require the stack size to be a multiple of the system page size, so round up. stack_size = RoundUp(stack_size, kPageSize); return stack_size; }
// static const size_t kStackOverflowImplicitCheckSize = 8 * KB; 上面kStackOverflowImplicitCheckSize的值是8k,而前面是1m,1024k+8k+8k=1040k,这就是为什么crash信息里面java.lang.OutOfMemoryError pthread_create (1040KB stack) failed: Out of memory是1040kb的原因。
- java中的每一个线程都都应一个JNIEnv结构,这里的JNIEnvExt就是ART中的JNIEnv。下面的注释说明的很明白,这里可能会有oom,这里具体要看JNIEnvExt::Create()方法 ``` const JNINativeInterface* JNIEnvExt::tableoverride = nullptr;
JNIEnvExt JNIEnvExt::Create(Thread self_in, JavaVMExt vm_in, std::string error_msg) {
// 调用new JNIEnvExt构造函数
std::unique_ptr
代码中发现特确实会返回nullptr,只有在CheckLocalsValid(ret.get())返回false的时候才会
bool JNIEnvExt::CheckLocalsValid(JNIEnvExt* in) NOTHREAD_SAFETY_ANALYSIS { if (in == nullptr) { return false; } return in->locals.IsValid(); }
从代码上看,基本排除是传入的参数nullptr导致的,所以根本原因是locals.IsValid返回了false,而locals是JNIEnvExt的一个成员变量,在JNIEnvExt构造的时候通过成员列表方式初始化
JNIEnvExt::JNIEnvExt(Thread self_in, JavaVMExt vmin, std::string* error_msg) : self(selfin), vm(vmin), local_ref_cookie(kIRTFirstSegment), locals(kLocalsInitial, kLocal, IndirectReferenceTable::ResizableCapacity::kYes, error_msg), monitors("monitors", kMonitorsInitial, kMonitorsMax), critical(0), check_jni(false), runtimedeleted(false) { MutexLock mu(Thread::Current(), *Locks::jnifunction_table_lock); checkjni = vmin->IsCheckJniEnabled(); functions = GetFunctionTable(check_jni); uncheckedfunctions = GetJniNativeInterface(); }
而[locals_.isValid](https://android.googlesource.com/platform/art/+/refs/tags/android-9.0.0_r41/runtime/indirect_reference_table.cc)的方法的源码为:
bool IndirectReferenceTable::IsValid() const { return tablemem_map.get() != nullptr; }
所以只可能是table_men_map为nullptr导致的。
而[IndirectReferenceTable](https://android.googlesource.com/platform/art/+/refs/tags/android-9.0.0_r41/runtime/indirect_reference_table.cc)类,他的构造函数为
IndirectReferenceTable::IndirectReferenceTable(sizet max_count,
IndirectRefKind desired_kind,
ResizableCapacity resizable,
std::string* error_msg)
: segment_state(kIRTFirstSegment),
kind(desired_kind),
max_entries(maxcount),
current_num_holes(0),
resizable(resizable) {
CHECK(error_msg != nullptr);
CHECK_NE(desired_kind, kHandleScopeOrInvalid);
// Overflow and maximum check.
CHECK_LE(max_count, kMaxTableSizeInBytes / sizeof(IrtEntry));
// max_count是常量512,而sizeof(IrtEntry)是8,所以table_bytes = 512 8 = 4k
const size_t table_bytes = max_count sizeof(IrtEntry);
table_mem_map.reset(MemMap::MapAnonymous("indirect ref table", nullptr, tablebytes,
PROT_READ | PROT_WRITE, false, false, error_msg));
if (table_mem_map.get() == nullptr && errormsg->empty()) {
*error_msg = "Unable to map memory for indirect ref table";
}
if (table_mem_map.get() != nullptr) {
table = reinterpret_cast
如果上面失败的话,那就只有一种情况就是 MemMap::MapAnonymous 失败了,而MemMap::MapAnonymous的作用是为JNIEnv结构体中的Indirect_Reference_table(C层用于存储JNI局部/全局变量)申请内存,我们继续看[MemMap](https://android.googlesource.com/platform/art/+/refs/tags/android-9.0.0_r41/runtime/mem_map.cc)
MemMap MemMap::MapAnonymous(const char name, uint8_t expected_ptr, size_t byte_count, int prot, bool low_4gb, bool reuse, std::string error_msg, bool use_ashmem) {
ifndef LP64
UNUSED(low_4gb);
endif
use_ashmem = use_ashmem && !kIsTargetLinux; if (byte_count == 0) { return new MemMap(name, nullptr, 0, nullptr, 0, prot, false); } size_t page_aligned_byte_count = RoundUp(byte_count, kPageSize); int flags = MAP_PRIVATE | MAP_ANONYMOUS; if (reuse) { // reuse means it is okay that it overlaps an existing page mapping. // Only use this if you actually made the page reservation yourself. CHECK(expected_ptr != nullptr); DCHECK(ContainedWithinExistingMap(expected_ptr, byte_count, error_msg)) << error_msg; flags |= MAP_FIXED; } if (use_ashmem) { if (!kIsTargetBuild) { // When not on Android (either host or assuming a linux target) ashmem is faked using // files in /tmp. Ensure that such files won't fail due to ulimit restrictions. If they // will then use a regular mmap. struct rlimit rlimit_fsize; CHECK_EQ(getrlimit(RLIMIT_FSIZE, &rlimit_fsize), 0); use_ashmem = (rlimit_fsize.rlim_cur == RLIM_INFINITY) || (page_aligned_byte_count < rlimit_fsize.rlim_cur); } } unique_fd fd; if (use_ashmem) { // android_os_Debug.cpp read_mapinfo assumes all ashmem regions associated with the VM are // prefixed "dalvik-". std::string debug_friendly_name("dalvik-"); debug_friendly_name += name; // 1. 创建 fd.reset(ashmem_create_region(debug_friendly_name.c_str(), page_aligned_byte_count)); // == -1 就说明是fd超过了系统限制的最大fd量,错误信息中会有Too many open files的提示 if (fd.get() == -1) { // We failed to create the ashmem region. Print a warning, but continue // anyway by creating a true anonymous mmap with an fd of -1. It is // better to use an unlabelled anonymous map than to fail to create a // map at all. PLOG(WARNING) << "ashmem_create_region failed for '" << name << "'"; } else { // We succeeded in creating the ashmem region. Use the created ashmem // region as backing for the mmap. flags &= ~MAP_ANONYMOUS; } } // We need to store and potentially set an error number for pretty printing of errors int saved_errno = 0; // 2. 调用mmap映射到用户态内存地址空间 void actual = MapInternal(expected_ptr, page_aligned_byte_count, prot, flags, fd.get(), 0, low_4gb); saved_errno = errno; if (actual == MAP_FAILED) { if (error_msg != nullptr) { if (kIsDebugBuild || VLOG_IS_ON(oat)) { PrintFileToLog("/proc/self/maps", LogSeverity::WARNING); } error_msg = StringPrintf("Failed anonymous mmap(%p, %zd, 0x%x, 0x%x, %d, 0): %s. " "See process maps in the log.", expected_ptr, page_aligned_byte_count, prot, flags, fd.get(), strerror(saved_errno)); } return nullptr; } if (!CheckMapRequest(expected_ptr, actual, page_aligned_byte_count, error_msg)) { return nullptr; } return new MemMap(name, reinterpret_cast<uint8_t>(actual), byte_count, actual, page_aligned_byte_count, prot, reuse); }
这里面又用到了`ashmem_create_region()`方法,该方法的作用就是创建一块匿名共享内存(Anonymous Shared Memory-Ashmem),并返回一个文件描述符,我们看一下[ashmem_create_region](https://android.googlesource.com/platform/system/core/+/4f6e8d7a00cbeda1e70cc15be9c4af1018bdad53/libcutils/ashmem-dev.c)的源码:
/*
- ashmem_create_region - creates a new ashmem region and returns the file
- descriptor, or <0 on error *
- `name' is an optional label to give the region (visible in /proc/pid/maps)
- `size' is the size of the region, in page-aligned bytes
/
int ashmem_create_region(const char name, size_t size)
{
int fd, ret;
// 打开一个fd
fd = open(ASHMEM_DEVICE, O_RDWR);
if (fd < 0)
if (name) {return fd;
} ret = ioctl(fd, ASHMEM_SET_SIZE, size); if (ret < 0)char buf[ASHMEM_NAME_LEN]; strlcpy(buf, name, sizeof(buf)); ret = ioctl(fd, ASHMEM_SET_NAME, buf); if (ret < 0) goto error;
return fd; error: close(fd); return ret; } ```goto error;
上面的两个步骤中,不论第一个步骤执行成功与否,都会执行第二步,但是执行的行为不同
- 如果第一步执行成功,就会通过Andorid的匿名共享内存(Anonymous Shared Memory)分配4KB(一个page)内核态内存,然后再通过Linux的mmap调用映射到用户态虚拟内存地址空间。
- 如果第一步执行失败,第二步就会通过Linux的mmap调用创建一段虚拟内存。
而上面失败的情况主要有:
- 第一步失败的情况一般是内核分配内存失败,这种情况下,整个设备OS的内存应该都处于非常紧张的状态。但是我们从crash的信息里面看用户的内存还是挺充足的,所以排除这种情况。
- 第二步失败的情况一般是进程虚拟内存地址空间耗尽。而且会打印Failed anonymous mmap的错误
所以这里child_jni_env_ext.get() == nullptr 通常是因为第二步失败,也就是进程虚拟内存地址空间耗尽。所以这就是代号JNIEnv OOM的原因。
__BIONIC_ERRDEF( ENOMEM , 12, "Out of memory" )
__BIONIC_ERRDEF( EMFILE , 24, "Too many open files" )
当然代号JNIEnv还有一种原因就是FD打开太多,到达了最大限制。
- child_jni_env_ext.get() != nullptr 才会继续
- 调用pthread_create创建线程,并返回结果
看一下pthread_create的代码
上面第一步中__allocate_thread方法的源码为:__BIONIC_WEAK_FOR_NATIVE_BRIDGE int pthread_create(pthread_t* thread_out, pthread_attr_t const* attr, void* (*start_routine)(void*), void* arg) { ErrnoRestorer errno_restorer; pthread_attr_t thread_attr; if (attr == NULL) { pthread_attr_init(&thread_attr); } else { thread_attr = *attr; attr = NULL; // Prevent misuse below. } pthread_internal_t* thread = NULL; void* child_stack = NULL; // 1. 分配该线程对应的栈内存空间,如果返回result != 0 就直接返回result就说明失败了 int result = __allocate_thread(&thread_attr, &thread, &child_stack); if (result != 0) { return result; } // Create a lock for the thread to wait on once it starts so we can keep // it from doing anything until after we notify the debugger about it // // This also provides the memory barrier we need to ensure that all // memory accesses previously performed by this thread are visible to // the new thread. thread->startup_handshake_lock.init(false); thread->startup_handshake_lock.lock(); thread->start_routine = start_routine; thread->start_routine_arg = arg; thread->set_cached_pid(getpid()); int flags = CLONE_VM | CLONE_FS | CLONE_FILES | CLONE_SIGHAND | CLONE_THREAD | CLONE_SYSVSEM | CLONE_SETTLS | CLONE_PARENT_SETTID | CLONE_CHILD_CLEARTID; void* tls = reinterpret_cast<void*>(thread->tls); #if defined(__i386__) // On x86 (but not x86-64), CLONE_SETTLS takes a pointer to a struct user_desc rather than // a pointer to the TLS itself. user_desc tls_descriptor; __init_user_desc(&tls_descriptor, false, tls); tls = &tls_descriptor; #endif // 2. linux系统调用clone,执行真正的创建动作,而这个clone是创建新进程,Unix里面其实只有进程,而线程是POSIX标准定义的,因此这里的clone只是实现线程的一种手段。 clone后父进程和子进程共享内存, 因此当两个进程的内存共享之后,完全就符合“线程”的定义了。 int rc = clone(__pthread_start, child_stack, flags, thread, &(thread->tid), tls, &(thread->tid)); if (rc == -1) { int clone_errno = errno; // We don't have to unlock the mutex at all because clone(2) failed so there's no child waiting to // be unblocked, but we're about to unmap the memory the mutex is stored in, so this serves as a // reminder that you can't rewrite this function to use a ScopedPthreadMutexLocker. thread->startup_handshake_lock.unlock(); if (thread->mmap_size != 0) { munmap(thread->attr.stack_base, thread->mmap_size); } // clone失败就会报出clone failed的错误 async_safe_format_log(ANDROID_LOG_WARN, "libc", "pthread_create failed: clone failed: %s", strerror(clone_errno)); return clone_errno; } int init_errno = __init_thread(thread); if (init_errno != 0) { // Mark the thread detached and replace its start_routine with a no-op. // Letting the thread run is the easiest way to clean up its resources. atomic_store(&thread->join_state, THREAD_DETACHED); __pthread_internal_add(thread); thread->start_routine = __do_nothing; thread->startup_handshake_lock.unlock(); return init_errno; } // Publish the pthread_t and unlock the mutex to let the new thread start running. *thread_out = __pthread_internal_add(thread); thread->startup_handshake_lock.unlock(); return 0; }
而__create_thread_mapped_space方法的源码为static int __allocate_thread(pthread_attr_t* attr, pthread_internal_t** threadp, void** child_stack) { size_t mmap_size; uint8_t* stack_top; if (attr->stack_base == NULL) { // The caller didn't provide a stack, so allocate one. // Make sure the stack size and guard size are multiples of PAGE_SIZE. if (__builtin_add_overflow(attr->stack_size, attr->guard_size, &mmap_size)) return EAGAIN; if (__builtin_add_overflow(mmap_size, sizeof(pthread_internal_t), &mmap_size)) return EAGAIN; mmap_size = __BIONIC_ALIGN(mmap_size, PAGE_SIZE); attr->guard_size = __BIONIC_ALIGN(attr->guard_size, PAGE_SIZE); // 调用mmap分配栈内存,而mmap分配的内存赋值给了stack_base, stack_base不光是线程执行的栈,其中还存储了线程的其他信息(线程名、ThreadLocal变量等,这些信息都定义在pthread_internal_t结构体中),而这个具体的大小就是前面我们分析的 1M + 8K + 8K = 1040K attr->stack_base = __create_thread_mapped_space(mmap_size, attr->guard_size); if (attr->stack_base == NULL) { return EAGAIN; } stack_top = reinterpret_cast<uint8_t*>(attr->stack_base) + mmap_size; } else { // Remember the mmap size is zero and we don't need to free it. mmap_size = 0; stack_top = reinterpret_cast<uint8_t*>(attr->stack_base) + attr->stack_size; } // Mapped space(or user allocated stack) is used for: // pthread_internal_t // thread stack (including guard) // To safely access the pthread_internal_t and thread stack, we need to find a 16-byte aligned boundary. stack_top = reinterpret_cast<uint8_t*>( (reinterpret_cast<uintptr_t>(stack_top) - sizeof(pthread_internal_t)) & ~0xf); pthread_internal_t* thread = reinterpret_cast<pthread_internal_t*>(stack_top); if (mmap_size == 0) { // If thread was not allocated by mmap(), it may not have been cleared to zero. // So assume the worst and zero it. memset(thread, 0, sizeof(pthread_internal_t)); } attr->stack_size = stack_top - reinterpret_cast<uint8_t*>(attr->stack_base); thread->mmap_size = mmap_size; thread->attr = *attr; if (!__init_tls(thread)) { if (thread->mmap_size != 0) munmap(thread->attr.stack_base, thread->mmap_size); return EAGAIN; } __init_thread_stack_guard(thread); *threadp = thread; *child_stack = stack_top; return 0; }static void* __create_thread_mapped_space(size_t mmap_size, size_t stack_guard_size) { // Create a new private anonymous map. int prot = PROT_READ | PROT_WRITE; // MAP_ANONYMOUS即匿名内存映射是在Linux中分配大块内存的常用方式。其分配的是虚拟内存,对应页的物理内存并不会立即分配,而是在用到的时候,触发内核的缺页中断,然后中断处理函数再分配物理内存。 int flags = MAP_PRIVATE | MAP_ANONYMOUS | MAP_NORESERVE; void* space = mmap(NULL, mmap_size, prot, flags, -1, 0); if (space == MAP_FAILED) { async_safe_format_log(ANDROID_LOG_WARN, "libc", "pthread_create failed: couldn't allocate %zu-bytes mapped space: %s", mmap_size, strerror(errno)); return NULL; } // Stack is at the lower end of mapped space, stack guard region is at the lower end of stack. // Set the stack guard region to PROT_NONE, so we can detect thread stack overflow. if (mprotect(space, stack_guard_size, PROT_NONE) == -1) { async_safe_format_log(ANDROID_LOG_WARN, "libc", "pthread_create failed: couldn't mprotect PROT_NONE %zu-byte stack guard region: %s", stack_guard_size, strerror(errno)); munmap(space, mmap_size); return NULL; } return space; }
而对于结果不为0的情况,那就只能是这里mmap分配虚拟内存失败。 所以代号1040的OOM也是因为虚拟内存分配失败导致的。
- 结果为0才是创建成功
调用ThrowOutOfMemoryError报出错误信息 如果child_jni_env_ext.get() == nullptr则报"Could not allocate JNI Env: %s", error_msg.c_str()的错误 否则如果pthread_create_result != 0则报"pthread_create (%s stack) failed: %s"
void Thread::ThrowOutOfMemoryError(const char* msg) { LOG(ERROR) << StringPrintf("Throwing OutOfMemoryError \"%s\"%s", msg, (throwing_OutOfMemoryError_ ? " (recursive case)" : "")); ThrowLocation throw_location = GetCurrentLocationForThrow(); if (!throwing_OutOfMemoryError_) { throwing_OutOfMemoryError_ = true; ThrowNewException(throw_location, "Ljava/lang/OutOfMemoryError;", msg); throwing_OutOfMemoryError_ = false; } else { Dump(LOG(ERROR)); // The pre-allocated OOME has no stack, so help out and log one. SetException(throw_location, Runtime::Current()->GetPreAllocatedOutOfMemoryError()); } }
最后总结一下: 不管是代号JNIEnv还是1040的OOM都是因为进程内虚拟内存地址空间耗尽导致的。
在一个32位系统中,如果是4G的内存空间,系统内核将使用最上层的1G虚拟空间,用户空间的内存就只剩下3G或者更少,而创建一个进程需要1040k的虚拟内存,所以假设创建一个线程什么都不干,那最多也只能最大能创建3000个线程。当逻辑地址空间不足(已用逻辑空间地址可以查看 /proc/pid/status中的VmPeak/VmSize查看),就会报出创建线程的OOM问题,W/libc: pthread_create failed: couldn't allocate 1069056-bytes mapped space: Out of memory
W/art: Throwing OutOfMemoryError "pthread_create (1040KB stack) failed: Try again"
而我在项目中遇到的问题是第二个也就是线程过多导致的,Android系统基于linux,所以linux的限制对Android同样实用,
- cat /proc/sys/kernel/threads-max 规定了每个进程创建线程数量的上限
验证:创建大量空线程,不做任何事情,直接sleep.
private Runnable emptyRunnable = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
for (int i = 0; i < 3000 ; i++) {
Thread.sleep(Long.MAX_VALUE);
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
};
连接手机
adb shell
ps -A -l
1 S 0 15304 2 0 19 0 - 0 0 ? 00:00:00 kworker/7:2
5 S 1000 15701 1001 0 19 0 - 1092845 0 ? 00:00:00 ndroid.keychain
5 S 10458 15834 1001 0 29 -10 - 1100514 0 ? 00:00:02 com.example.oom
5 S 10014 15956 1001 0 19 0 - 1106511 0 ? 00:00:01 com.android.mms
1 S 0 16275 2 0 19 0 - 0 0 ? 00:00:00 kworker/1:2
1 S 0 16542 2 0 19 0 - 0 0 ? 00:00:00 kworker/3:2
1 S 0 16603 2 0 19 0 - 0 0 ? 00:00:00 kworker/2:2
pid为15834
cat proc/15834/status
PD1806:/ $ cat proc/15834/status
Name: com.example.oom
Umask: 0077
State: S (sleeping)
Tgid: 15834 // 进程组的ID
Ngid: 0
Pid: 15834 // 进程ID
PPid: 1001 // 当前进程的父进程
TracerPid: 0 // 跟踪当前进程的进程ID,如果是0表示没有跟踪
Uid: 10458 10458 10458 10458
Gid: 10458 10458 10458 10458
FDSize: 128 // 当前分配的文件描述符,这个值不是当前进程使用文件描述符的上线
Groups: 9997 20458 50458
VmPeak: 4403108 kB // 当前进程运行过程中所占用内存的峰值
VmSize: 4402056 kB // 已用逻辑空间地址,虚拟内存大小。整个进程使用虚拟内存大小,是VmLib, VmExe, VmData, 和 VmStk的总和。
VmLck: 0 kB
VmPin: 0 kB
VmHWM: 49108 kB // 程序得到分配到物理内存的峰值
VmRSS: 48920 kB // 程序现在正在使用的物理内存
RssAnon: 9268 kB
RssFile: 39540 kB
RssShmem: 112 kB
VmData: 1737808 kB // 所占用的虚拟内存
VmStk: 8192 kB // 任务在用户态的栈的大小 (stack_vm)
VmExe: 20 kB // 程序所拥有的可执行虚拟内存的大小,代码段,不包括任务使用的库 (end_code-start_code)
VmLib: 163804 kB // 被映像到任务的虚拟内存空间的库的大小 (exec_lib)
VmPTE: 1000 kB // 该进程的所有页表的大小,单位:kb
VmPMD: 32 kB
VmSwap: 15776 kB
Threads: 17 // 当前的线程数
SigQ: 0/21568
SigPnd: 0000000000000000
ShdPnd: 0000000000000000
SigBlk: 0000000000001204
SigIgn: 0000000000000000
SigCgt: 00000006400084f8
CapInh: 0000000000000000
CapPrm: 0000000000000000
CapEff: 0000000000000000
CapBnd: 0000000000000000
CapAmb: 0000000000000000
Seccomp: 2
Cpus_allowed: ff
Cpus_allowed_list: 0-7
Mems_allowed: 1
Mems_allowed_list: 0
voluntary_ctxt_switches: 2132
nonvoluntary_ctxt_switches: 328
当线程数(可以在/proc/pid/status 中的threads项实时查看)超过/proc/sys/kernel/threads-max 中规定的上限时产生 OOM 崩溃。
定位验证方法:
Thread.UncaughtExceptionHandler捕获到OutOfMemoryError时记录/proc/pid目录下的如下信息:
- /proc/pid/fd目录下文件数(fd数)
- /proc/pid/status中threads项(当前线程数目)
- 当前设备的内存信息
- OOM的日志信息(出了堆栈信息还包含其他的一些warning信息
- 在灰度版本中通过一个定时器10分钟dump出应用所有的线程,当线程数超过一定阈值时,将当前的线程上报并预警,通过对这种异常情况的捕捉
什么情况下虚拟内存地址空间才会耗尽
说面分析了那么多,结论就是因为虚拟内存空间耗尽导致的,但是究竟什么情况才会出现耗尽的情况?
内存是程序运行时的存储地址空间,可分为虚拟地址空间和物理地址空间。虚拟地址空间是相对进程而言的,每个进程都有独立的地址空间(如32位程序都有4GB的虚拟地址空间)。物理地址空间就是由硬件(内存条)提供的存储空间,物理地址空间被所有进程共享。
Linux采用虚拟内存管理技术,每个进程都有各自独立的进程地址空间(即4G的线性虚拟空间),无法直接访问物理内存。这样起到保护操作系统,并且让用户程序可使用比实际物理内存更大的地址空间。
4G进程地址空间被划分两部分,内核空间和用户空间。用户空间(包括代码、数据、堆、共享库以及栈)从0到3G,内核空间(包括内核中的代码和数据结构)从3G到4G;
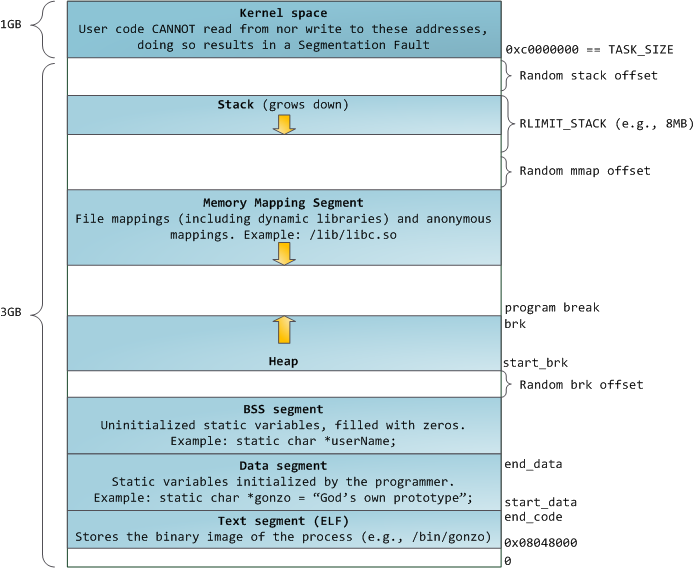
用户进程通常情况只能访问用户空间的虚拟地址,不能访问内核空间虚拟地址。只有用户进程进行系统调用(代表用户进程在内核态执行)等情况可访问到内核空间; 用户空间对应进程,所以当进程切换,用户空间也会跟着变化; 内核空间是由内核负责映射,不会跟着进程变化;内核空间地址有自己对应的页表,用户进程各自有不同额页表。
从程序角度看,我们谈到的地址空间一般是虚拟地址空间,通过malloc或new分配的内存都虚拟地址空间的内存。虚拟地址空间与物理地址空间的都是以page为最小管理单元,page的大小因系统而异,一般都是4KB。虚拟地址空间有到物理地址空间的映射,如果要访问的虚拟地址空间没有映射到物理地址空间,操作系统会产生缺页中断,将虚拟地址空间映射到物理地址空间。
因此,程度的虚拟地址空间比物理的地址空间要大的多。在较多进程同时运行时,物理地址空间有可能不够,操作系统会将一部物理地址空间的内容交换到磁盘,从而腾挪出一部分物理地址空间来。磁盘上的交换区,在linux上叫swap area,windows时叫page file。
android底层基于linux,不过android是没有交换区的(为什么没有?),所以android系统的内存资源就更加宝贵。为更合理、充分利用有限内存资源,android引入一个low-memory-killer机制,在内存不足,根据规则回收一部分低优先级的进程,从而释放他们占有的内存。
进程的内存空间只是虚拟内存,而程序运行需要的是物理内存(ram),在必要时,操作系统会将程序运行中申请的虚拟内存映射到ram,让进程能够使用物理内存。进程所操作的空间都是虚拟地址空间,无法直接操作ram。java程序发生OOM并不表示ram不足,如果ram真的不足,android的memory killer就会发挥作用,它会杀死一些优先级比较低的进程来释放物理内存,让高优先级程序得到更多的内存。
Android系统给每个进程分配了一定的虚拟地址空间大小,进程使用的虚拟空间如果超过阈值,就会触发OOM。所以只可能是线程太多,消耗了大部分虚拟内存地址空间,从而引发了当前进程空间不足。
adb shell dumpsys meminfo packagename 可以查看占用的内存信息
PD1806:/system/bin $ dumpsys meminfo com.example.oom
Applications Memory Usage (in Kilobytes):
Uptime: 31807223 Realtime: 31807223
** MEMINFO in pid 11380 [com.example.oom] **
Pss Private Private SwapPss Heap Heap Heap
Total Dirty Clean Dirty Size Alloc Free
------ ------ ------ ------ ------ ------ ------
Native Heap 64227 64176 0 28 77824 72483 5340
Dalvik Heap 2158 2124 0 24 3590 2693 897
Dalvik Other 20804 20804 0 0
Stack 92 92 0 0
Ashmem 2 0 0 0
Gfx dev 892 892 0 0
Other dev 12 0 12 0
.so mmap 8595 212 6180 16
.apk mmap 2388 1964 60 0
.ttf mmap 105 0 0 0
.dex mmap 2375 176 552 0
.oat mmap 176 0 112 0
.art mmap 6796 6356 120 0
Other mmap 60 4 4 0
EGL mtrack 29808 29808 0 0
GL mtrack 3000 3000 0 0
Unknown 44350 44332 0 1
TOTAL 185909 173940 7040 69 81414 75176 6237
App Summary
Pss(KB)
------
Java Heap: 8600
Native Heap: 64176
Code: 9256
Stack: 92
Graphics: 33700
Private Other: 65156
System: 4929
TOTAL: 185909 TOTAL SWAP PSS: 69
Objects
Views: 27 ViewRootImpl: 1
AppContexts: 5 Activities: 1
Assets: 7 AssetManagers: 0
Local Binders: 14 Proxy Binders: 31
Parcel memory: 4 Parcel count: 20
Death Recipients: 1 OpenSSL Sockets: 0
WebViews: 0
SQL
MEMORY_USED: 0
PAGECACHE_OVERFLOW: 0 MALLOC_SIZE: 0
查看当前手机的内存信息可以通过cat /proc/meminfo来查看
1|PD1806:/ $ cat /proc/meminfo
MemTotal: 5772000 kB
MemFree: 129500 kB
MemAvailable: 2594764 kB
Buffers: 3968 kB
Cached: 2330100 kB
SwapCached: 12780 kB
Active: 2678740 kB
Inactive: 759120 kB
Active(anon): 804284 kB
Inactive(anon): 303532 kB
Active(file): 1874456 kB
Inactive(file): 455588 kB
Unevictable: 3500 kB
Mlocked: 3500 kB
SwapTotal: 2097148 kB
SwapFree: 488020 kB
Dirty: 60 kB
Writeback: 0 kB
AnonPages: 1102064 kB
Mapped: 743796 kB 映射文件大小
Shmem: 1416 kB
Slab: 548448 kB
SReclaimable: 241428 kB
SUnreclaim: 307020 kB
KernelStack: 171856 kB
PageTables: 108432 kB
NFS_Unstable: 0 kB
Bounce: 0 kB
WritebackTmp: 0 kB
CommitLimit: 4983148 kB // 请的内存总数超过这个阈值就算overcommit,CommitLimit 就是overcommit的阈值,申请的内存总数超过CommitLimit的话就算是overcommit。
Committed_AS: 131533804 kB // 表示所有进程已经申请的内存总大小,(注意是已经申请的,不是已经分配的),如果 Committed_AS 超过 CommitLimit 就表示发生了 overcommit,超出越多表示 overcommit 越严重。Committed_AS 的含义换一种说法就是,如果要绝对保证不发生OOM (out of memory) 需要多少物理内存。
VmallocTotal: 263061440 kB
VmallocUsed: 0 kB
VmallocChunk: 0 kB
CmaTotal: 217088 kB
CmaFree: 1740 kB
NR_KMALLOC: 23312 kB
NR_VMALLOC: 33844 kB
NR_DMA_NOR: 0 kB
NR_DMA_CMA: 58348 kB
NR_ION: 268600 kB
free_ion: 121060 kB
free_ion_pool: 121060 kB
free_ion_heap: 0 kB
NR_GPU: 267812 kB
free_gpu: 154260 kB
zram_size: 609440 kB
zcache_size: 0 kB
pcppages: 6944 kB
ALL_MEM: 5675448 kB
- Virtual Memory and Linux
- Android进程的内存管理分析
- Android系统匿名共享内存(Anonymous Shared Memory)C++调用接口分析
- Android系统匿名共享内存Ashmem(Anonymous Shared Memory)驱动程序源代码分析
- Android系统匿名共享内存Ashmem(Anonymous Shared Memory)简要介绍和学习计划
- 虚拟内存那点事
- 邮箱 :[email protected]
- Good Luck!